Atelectasis and Pneumonia vs. Asthma
Marketing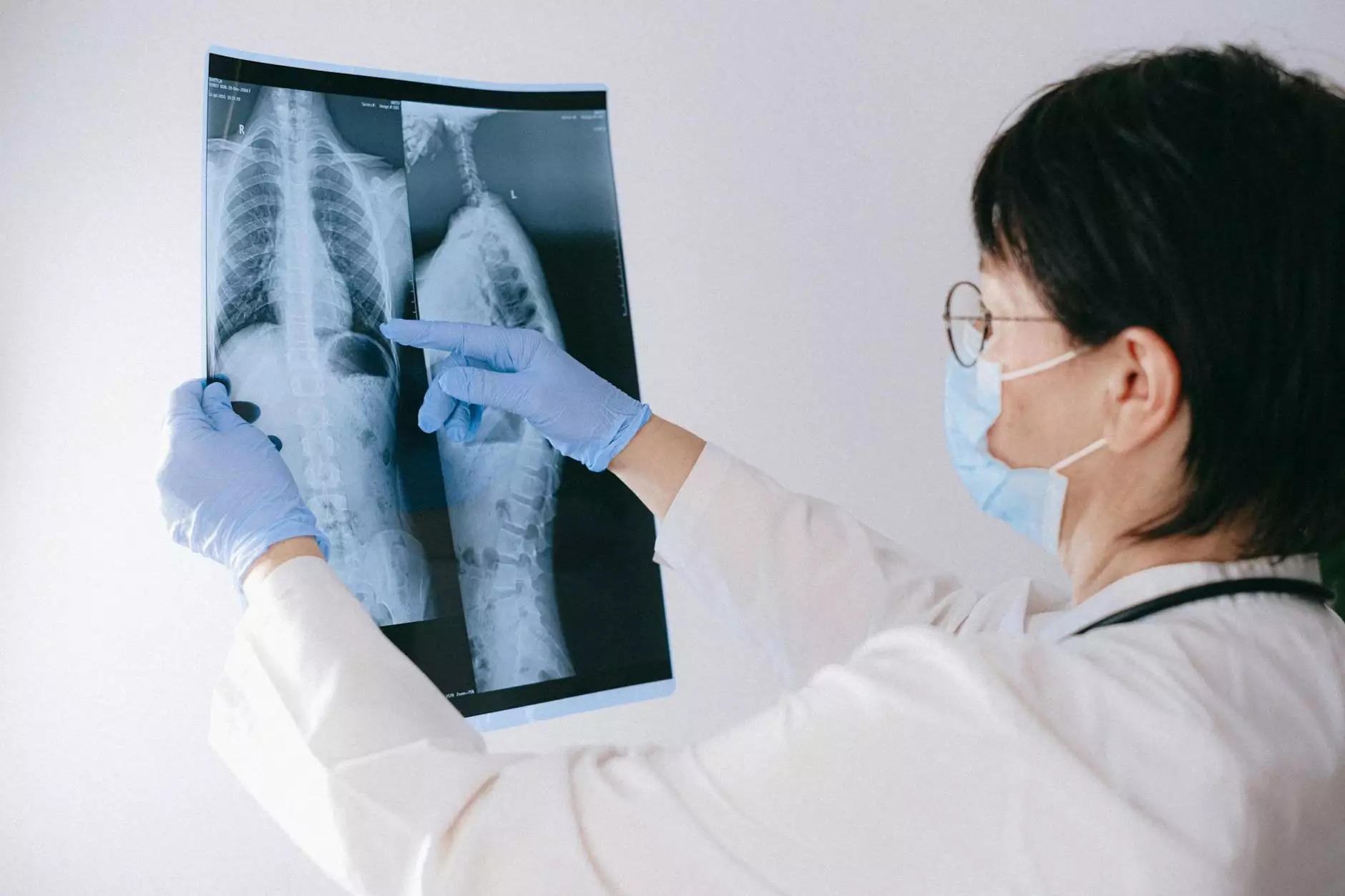
Understanding Atelectasis versus Pneumonia
When discussing respiratory conditions, atelectasis and pneumonia are two terms that are often mentioned. While both conditions affect the lungs, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is a condition that occurs when one or more areas of the lungs collapse or are not fully inflated. This can be caused by various factors such as blockages in the airways, pressure from outside the lungs, or surfactant deficiency.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia, on the other hand, is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and leads to symptoms such as cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
Key Differences Between Atelectasis and Pneumonia
- Causes: Atelectasis is often caused by lung blockages or external pressure, while pneumonia is typically caused by infectious agents.
- Symptoms: Atelectasis may be asymptomatic or present with mild symptoms, whereas pneumonia is characterized by more severe symptoms like high fever and productive cough.
- Treatment: Atelectasis treatment focuses on re-expanding the affected lung areas, while pneumonia treatment involves antibiotics or antiviral medications.
Atelectasis versus Asthma
It's important to differentiate between atelectasis and asthma, another common respiratory condition. While atelectasis involves collapsed lung areas, asthma is a chronic inflammation of the airways leading to recurrent episodes of wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the distinctions between atelectasis, pneumonia, and asthma is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. If you or a loved one experience respiratory symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate evaluation and management.